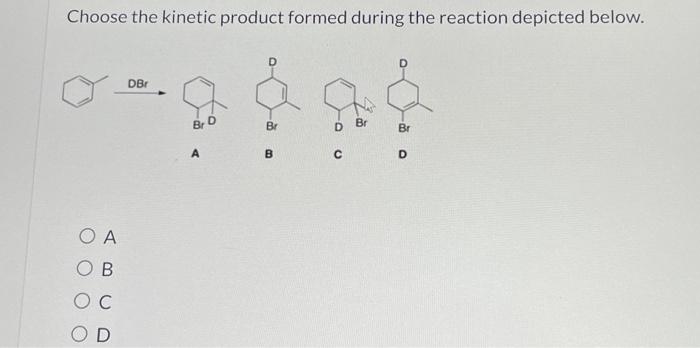
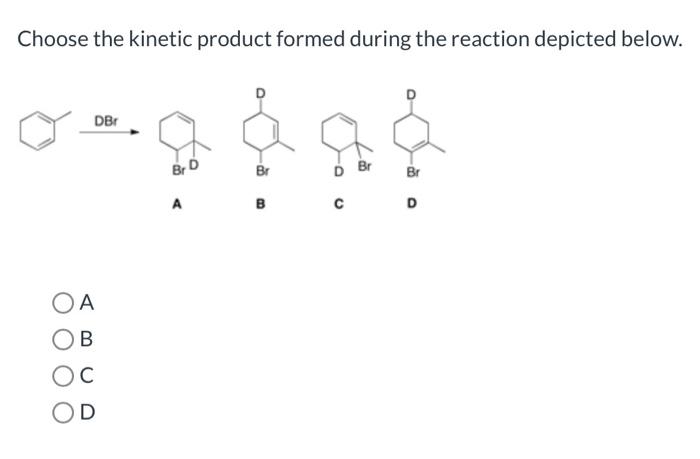
Choose the kinetic product formed during the reaction depicted below. – In the realm of organic chemistry, the concept of kinetic products takes center stage, inviting us to explore the intricacies of reaction outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, factors, methods, and applications of kinetic product formation, providing a roadmap for understanding and harnessing this fundamental aspect of organic synthesis.
Kinetic products, formed under reaction conditions that favor the lowest activation energy pathway, offer valuable insights into the dynamics of chemical transformations. Their formation is influenced by a myriad of factors, including temperature, pressure, solvent, concentration, and the nature of the reactants.
Understanding these factors empowers chemists to predict and control reaction outcomes, leading to regio- and stereoselective reactions, the synthesis of specific isomers, and the precise control of reaction outcomes.
Kinetic Product Formation
In organic chemistry, the kinetic product is the product that is formed faster under a given set of reaction conditions. It is the product that is formed from the transition state with the lowest activation energy.
Kinetic products are often less stable than the thermodynamic product, which is the product that is more stable under the given reaction conditions. However, kinetic products can be isolated if the reaction is quenched before the thermodynamic product has a chance to form.
Factors Affecting Kinetic Product Formation
- Reaction conditions:The temperature, pressure, and solvent can all affect the formation of kinetic products. Higher temperatures favor the formation of thermodynamic products, while lower temperatures favor the formation of kinetic products. Higher pressures can also favor the formation of kinetic products.
- Concentration of reactants:The concentration of reactants can also affect the formation of kinetic products. Higher concentrations of reactants favor the formation of kinetic products, while lower concentrations of reactants favor the formation of thermodynamic products.
- Nature of the reactants:The nature of the reactants can also affect the formation of kinetic products. Some reactants are more likely to form kinetic products than others.
Regio- and Stereoselectivity, Choose the kinetic product formed during the reaction depicted below.
Regio- and stereoselectivity are two important concepts in organic chemistry. Regioselectivity refers to the formation of a product at a specific atom or group of atoms. Stereoselectivity refers to the formation of a product with a specific stereochemistry.
Kinetic products are often regio- and stereoselective. This means that they are formed at a specific atom or group of atoms and with a specific stereochemistry.
Methods for Predicting Kinetic Product Formation
- Hammond’s postulate:Hammond’s postulate states that the transition state of a reaction resembles the structure of the product that is formed faster.
- Curtin-Hammett principle:The Curtin-Hammett principle states that the rate of a reaction is determined by the slowest step in the reaction mechanism.
- Transition state theory:Transition state theory is a theoretical model that can be used to predict the rate of a reaction and the structure of the transition state.
Applications of Kinetic Product Formation
- Regio- and stereoselective reactions:Kinetic product formation can be used to achieve regio- and stereoselective reactions. This is important in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
- Synthesis of specific isomers:Kinetic product formation can be used to synthesize specific isomers of a compound. This is important in the pharmaceutical industry, where different isomers of a drug can have different biological activities.
- Control of reaction outcomes:Kinetic product formation can be used to control the outcome of a reaction. This is important in the development of new synthetic methods.
FAQ Section: Choose The Kinetic Product Formed During The Reaction Depicted Below.
What is the definition of a kinetic product?
A kinetic product is the product of a chemical reaction that is formed under conditions that favor the lowest activation energy pathway, rather than the most stable product.
What factors influence the formation of kinetic products?
Factors that influence the formation of kinetic products include reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, solvent), concentration of reactants, and the nature of the reactants.
How can we predict the kinetic product of a reaction?
Methods used to predict the kinetic product of a reaction include Hammond’s postulate, the Curtin-Hammett principle, and transition state theory.
What are the applications of kinetic product formation?
Applications of kinetic product formation include regio- and stereoselective reactions, the synthesis of specific isomers, and the control of reaction outcomes in organic synthesis.