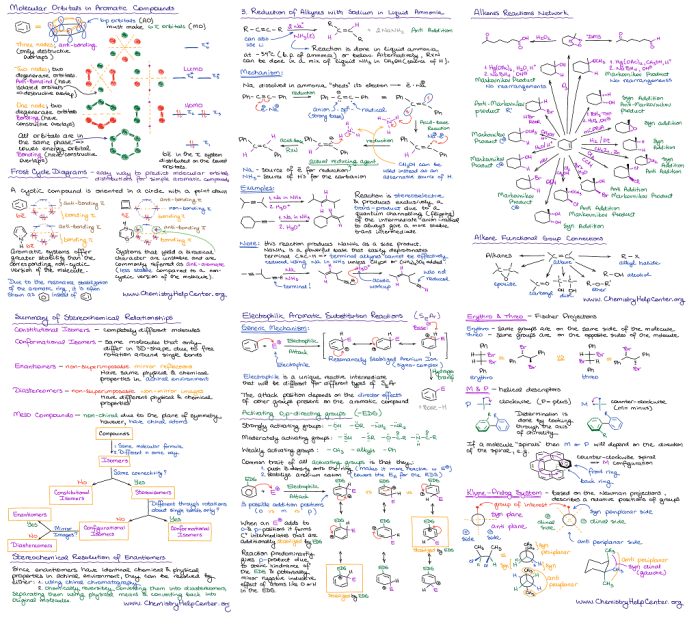
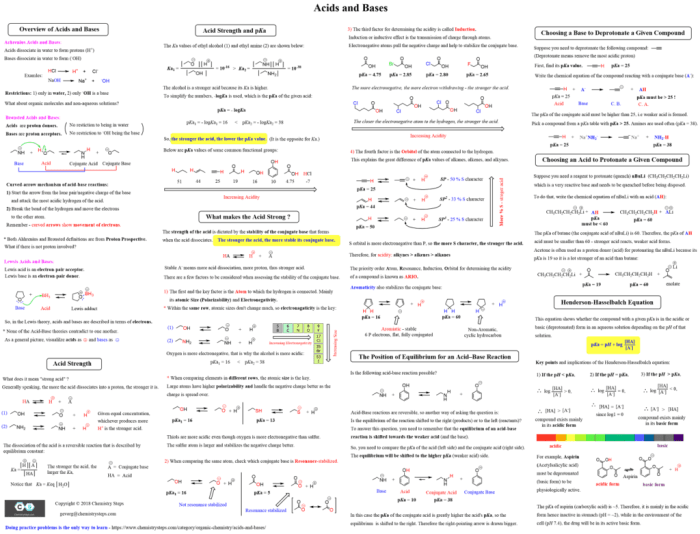
The Organic Chemistry Final Exam Cheat Sheet serves as an indispensable companion for students preparing for their final examination. This comprehensive guide encompasses the fundamental principles and concepts of organic chemistry, empowering learners with the knowledge and strategies necessary to excel in their studies.
Within this cheat sheet, students will find a concise yet thorough overview of organic chemistry, covering key concepts such as functional groups, bonding, and reaction mechanisms. It provides lucid explanations of common reaction mechanisms, including nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic addition, and radical reactions, highlighting the factors that influence their rate and selectivity.
Organic Chemistry Concepts
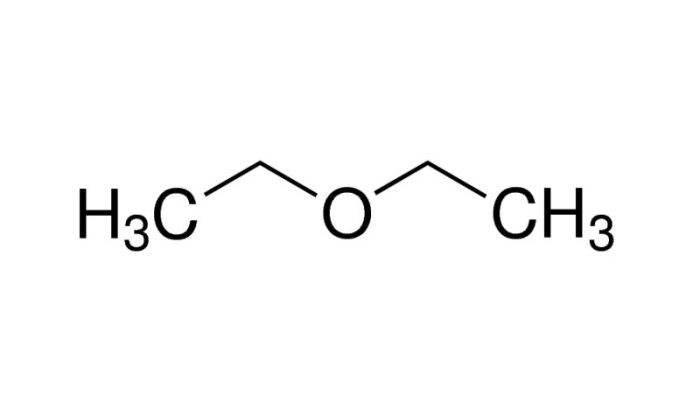
Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-containing compounds. Carbon is a unique element that can form a wide variety of bonds with itself and other elements, resulting in an enormous number of organic compounds.
Organic compounds are essential for life. They are found in all living organisms, and they play a vital role in many biological processes. Organic compounds are also used in a wide variety of products, including pharmaceuticals, plastics, and fuels.
The study of organic chemistry provides a foundation for understanding the chemistry of life and the development of new products and technologies.
Functional Groups, Organic chemistry final exam cheat sheet
Functional groups are groups of atoms that have characteristic chemical properties. Functional groups are responsible for the reactivity of organic compounds.
Some common functional groups include:
- Alkanes: Contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, and are saturated (all carbon atoms are bonded to four other atoms).
- Alkenes: Contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
- Alkynes: Contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
- Alcohols: Contain a hydroxyl group (-OH).
- Ethers: Contain an ether group (-O-).
- Aldehydes: Contain a carbonyl group (-CHO).
- Ketones: Contain a carbonyl group (-CO-).
- Carboxylic acids: Contain a carboxyl group (-COOH).
- Amines: Contain an amino group (-NH2).
Bonding
Organic compounds are held together by covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons.
The type of covalent bond that is formed depends on the number of electrons that are shared.
- Single bonds: Formed when two atoms share one pair of electrons.
- Double bonds: Formed when two atoms share two pairs of electrons.
- Triple bonds: Formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons.
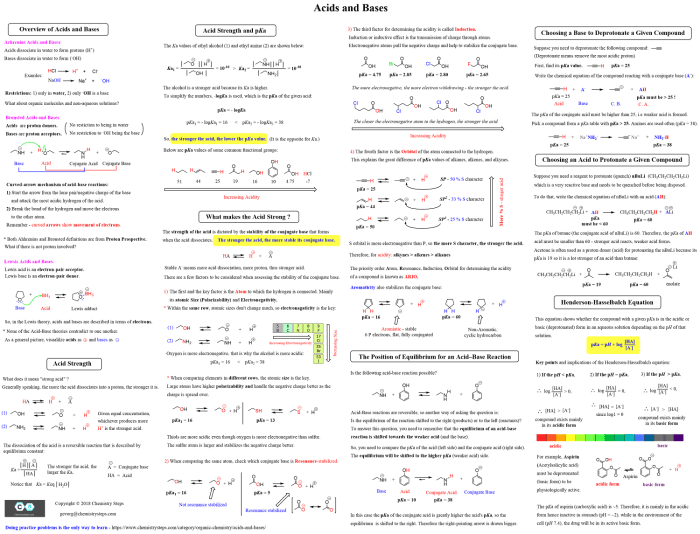
Reaction Mechanisms
Organic reactions are chemical reactions that involve organic compounds.
Organic reactions can be classified into two main types:
- Homolytic reactions: Reactions in which bonds are broken homolytically, resulting in the formation of free radicals.
- Heterolytic reactions: Reactions in which bonds are broken heterolytically, resulting in the formation of ions.
The type of reaction mechanism that occurs depends on the structure of the reactants and the reaction conditions.
FAQ Insights: Organic Chemistry Final Exam Cheat Sheet
What is the purpose of the Organic Chemistry Final Exam Cheat Sheet?
The Organic Chemistry Final Exam Cheat Sheet is designed to provide students with a concise and comprehensive overview of the essential concepts and techniques covered in an organic chemistry course, serving as a valuable study aid for the final examination.
What topics are covered in the cheat sheet?
The cheat sheet covers a wide range of topics in organic chemistry, including functional groups, bonding, reaction mechanisms, spectroscopy, synthesis, and characterization. It also includes practical tips and strategies for exam preparation.
How can I use the cheat sheet effectively?
The cheat sheet is intended to be used as a supplementary study tool. Students should review the material covered in class and their textbooks, then use the cheat sheet to reinforce their understanding and identify areas where they need additional focus.