Analytical writing assessment gmat sample – Introducing the Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA) GMAT sample, a crucial component of the Graduate Management Admission Test. This comprehensive guide delves into the structure, scoring criteria, and time constraints of the AWA sample, providing invaluable insights to enhance your performance.
The subsequent paragraphs will meticulously analyze the argument’s structure, assumptions, and biases, guiding you in developing a well-reasoned counterargument. Moreover, effective organization and writing techniques will be explored to ensure a coherent and persuasive response.
Overview of the Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA) GMAT Sample

The Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA) GMAT sample is a component of the Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) that evaluates candidates’ critical thinking and writing abilities. It presents a brief argument and prompts candidates to analyze and critique it, demonstrating their capacity to:
- Identify and evaluate the main argument and supporting points
- Assess the argument’s assumptions and potential biases
- Develop a well-reasoned counterargument
- Organize and write a coherent response
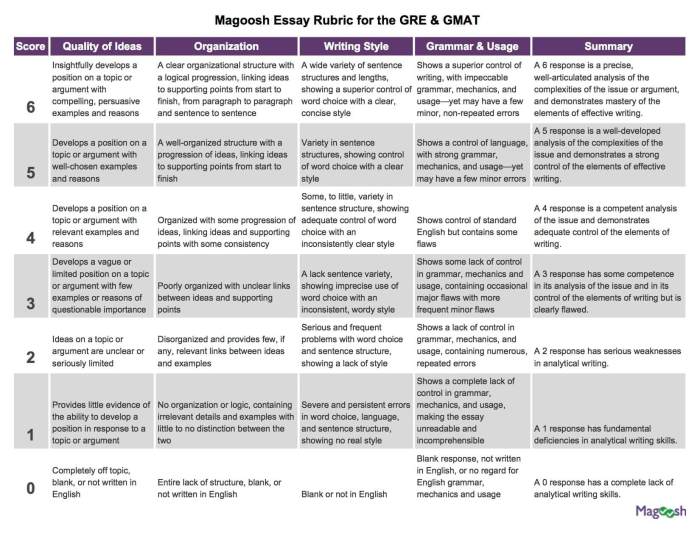
The AWA GMAT sample is timed, allowing 30 minutes for the analysis and writing process. It is scored on a scale of 0 to 6, with 0 being the lowest and 6 being the highest. The scoring criteria focus on:
- The clarity and effectiveness of the analysis
- The quality of the counterargument
- The overall organization and coherence of the response
Analyzing the Argument’s Structure
Identifying the Main Argument and Supporting Points
The first step in analyzing the argument is to identify the main argument. This is typically stated explicitly in the introduction or conclusion of the passage. Once the main argument is identified, candidates can then identify the supporting points that are used to support it.
Discussing the Logical Flow and Organization
Next, candidates should examine the logical flow and organization of the argument. They should consider how the supporting points are presented and how they relate to each other. They should also identify any logical fallacies or weaknesses in the argument’s structure.
Evaluating the Use of Evidence and Examples
Finally, candidates should evaluate the use of evidence and examples in the argument. They should consider whether the evidence is relevant and credible and whether the examples are appropriate and effective.
Assessing the Argument’s Assumptions and Biases: Analytical Writing Assessment Gmat Sample

Identifying Unstated Assumptions
Many arguments rely on unstated assumptions that are not explicitly stated in the text. Candidates should try to identify these assumptions and evaluate their validity. Assumptions that are not supported by evidence or that are not reasonable can weaken the argument.
Discussing Potential Biases or Limitations
Arguments can also be biased or limited in perspective. Candidates should consider whether the author has any biases or limitations that could affect the argument. They should also consider whether the argument takes into account all relevant perspectives and evidence.
Providing Evidence to Support or Refute Assumptions and Biases
Candidates should provide evidence to support or refute the assumptions and biases they identify. This evidence can come from the passage itself, from outside sources, or from their own knowledge and experience.
Developing a Counterargument
Designing a Well-Reasoned Counterargument, Analytical writing assessment gmat sample
Once the argument has been analyzed, candidates can begin to develop a counterargument. The counterargument should be well-reasoned and supported by evidence. It should also address the main points of the original argument.
Providing Supporting Evidence and Examples
The counterargument should be supported by evidence and examples. This evidence can come from the passage itself, from outside sources, or from the candidate’s own knowledge and experience.
Addressing Potential Objections
Candidates should anticipate potential objections to their counterargument and address them in their response. This will help to strengthen the counterargument and make it more persuasive.
FAQ Summary
What is the purpose of the AWA GMAT sample?
The AWA GMAT sample is designed to assess your critical thinking, analytical writing, and argumentation skills.
How is the AWA GMAT sample scored?
The AWA GMAT sample is scored on a scale of 0 to 6, with 6 being the highest score.
What are the time constraints for the AWA GMAT sample?
You will have 30 minutes to complete the AWA GMAT sample.